फैसियोला हिपैटिका के जीवन चक्र का सचित्र वर्णन
कीजिए ।
Describe the life cycle of Fasciola-hepatica
with diagram.
 |
| फैसियोला हिपैटिका के जीवन चक्र का सचित्र वर्णन कीजिए । The life cycle of Fasciola-hepatica |
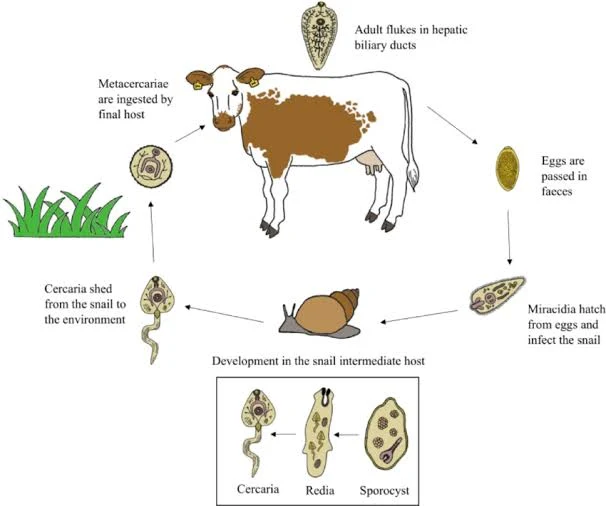
Life Cycle of Fasciola hepatica:
1. Egg Stage:
The life cycle begins with adult flukes residing in the liver of the host (commonly sheep, cattle, or other mammals). The flukes release eggs into the host's liver parenchyma.
2. Excretion of Eggs:
The eggs are excreted from the host through its feces. In water, these eggs embryonate, giving rise to miracidia.
3. Miracidia Stage:
The eggs hatch, releasing free-swimming larvae called miracidia. Miracidia are equipped with cilia for movement and seek out a suitable intermediate host, usually a snail.
4. Infection of Snail:
Once the miracidia find a suitable snail host, they penetrate its tissues and develop into sporocysts, rediae, and cercariae within the snail. This part of the life cycle occurs in the snail's hepatopancreas.
5. Cercariae Stage:
Cercariae are released from the snail and swim freely in water. They have a short life span during which they need to find and infect the definitive host, typically a herbivorous mammal.
6. Encystment on Vegetation:
Cercariae encyst on vegetation as metacercariae, forming a protective cyst. The cyst is ingested by the definitive host through grazing on contaminated vegetation.
7. Development in Definitive Host:
Once inside the definitive host's digestive system, the metacercariae excyst, and juvenile flukes migrate to the liver. In the liver, they mature into adult flukes, completing the life cycle.
The cycle then repeats as adult flukes release eggs in the host's liver, and the eggs are excreted to continue the process.
फैसिओला हेपैटिका का जीवन चक्र:
1. अंडे का स्थिति:
जीवन चक्र उस समय शुरू होता है जब वयस्क फ्ल्यूक्स मेजबान (सामान्यत: भेड़, गाय या अन्य स्तनधारित पशु) की जिगर में पाए जाते हैं। फ्ल्यूक्स यौन संगम के बाद मेजबान की जिगर के परेंकाइमा से अंडे रिहा करते हैं।
2. अंडों का निर्वाह:
ये अंडे मेजबान से उसके फेकेस के साथ बाहर आते हैं। पानी में, ये अंडे विकसित होते हैं, जिससे मिरासिडिया उत्पन्न होते हैं।
3. मिरासिडिया स्थिति:
अंडे खुलते हैं, मिरासिडिया नामक मुक्त-तैरते लार्वा मिलता है। मिरासिडिया चलने के लिए केशिका से लैस होता है और एक उपयुक्त इंटरमीडिएट मेजबान की तलाश करता है, आमतौर पर एक स्नेल।
4. स्नेल का संक्रमण:
जब मिरासिडिया उपयुक्त स्नेल मेजबान मिलता है, तो वह स्नेल के ऊतकों में प्रवेश करता है और उसके अंदर स्पोरोसिस्ट्स, रेडिए, और सरकेरिया में विकसित होता है। यह जीवन चक्र स्नेल के हेपेटोपैंक्रिएस में होता है।
5. सरकेरिया स्थिति:
सरकेरिया स्नेल से मुक्त होते हैं और पानी में तैरते हैं। इसकी जीवनकाल शॉर्ट होती है, जिसमें वह आखिरी मेजबान, सामान्यत: एक घासाहारी स्तनधारित स्तनधारक को खोजने और संक्रमित करने के लिए होते हैं।
6. ऊपरी वनस्पति पर आवर्तन:
सरकेरिया ऊपरी वनस्पति पर मेटासर्केरिया के रूप में आवर्तन करती है, एक सुरक्षित खाद बनाती है। खाद एक मुख्य मेजबान द्वारा उपभोजन के माध्यम से इंगेस्ट की जाती है।
7. मेजबान में विकास:
एक बार निर्धारित मेजबान के पाचन तंत्र में, मेटासर्केरिया बाहर निकलती हैं, और युवा फ्ल्यूक्स जिगर की ओर प्रवाहित होते हैं। जिगर में, वे वयस्क फ्ल्यूक्स में परिपूर्ण होते हैं, जीवन चक्र को पूर्ण करते हैं।
इसके बाद चक्र पुनः पेश होता है, जब वयस्क फ्ल्यूक्स मेजबान के जिगर में अंडे छोड़ते हैं, और ये अंडे पेशाब के माध्यम से बाहर आते हैं ताकि प्रक्रिया जारी रह सके।













2 Comments
Nice
ReplyDeleteThanks Uniexpro
ReplyDelete